Daily Life and Nutritional Needs of Domestic Animals
Domestic animals have become an integral part of human society, enriching lives through companionship and various roles. Understanding their daily routines, behavioral patterns, and specific nutritional requirements is crucial for ensuring their well-being. This article explores the fundamental aspects of caring for domestic animals, focusing on how their environment, diet, and interaction contribute to their overall health and happiness, fostering a stronger bond between pets and their human counterparts across the globe.
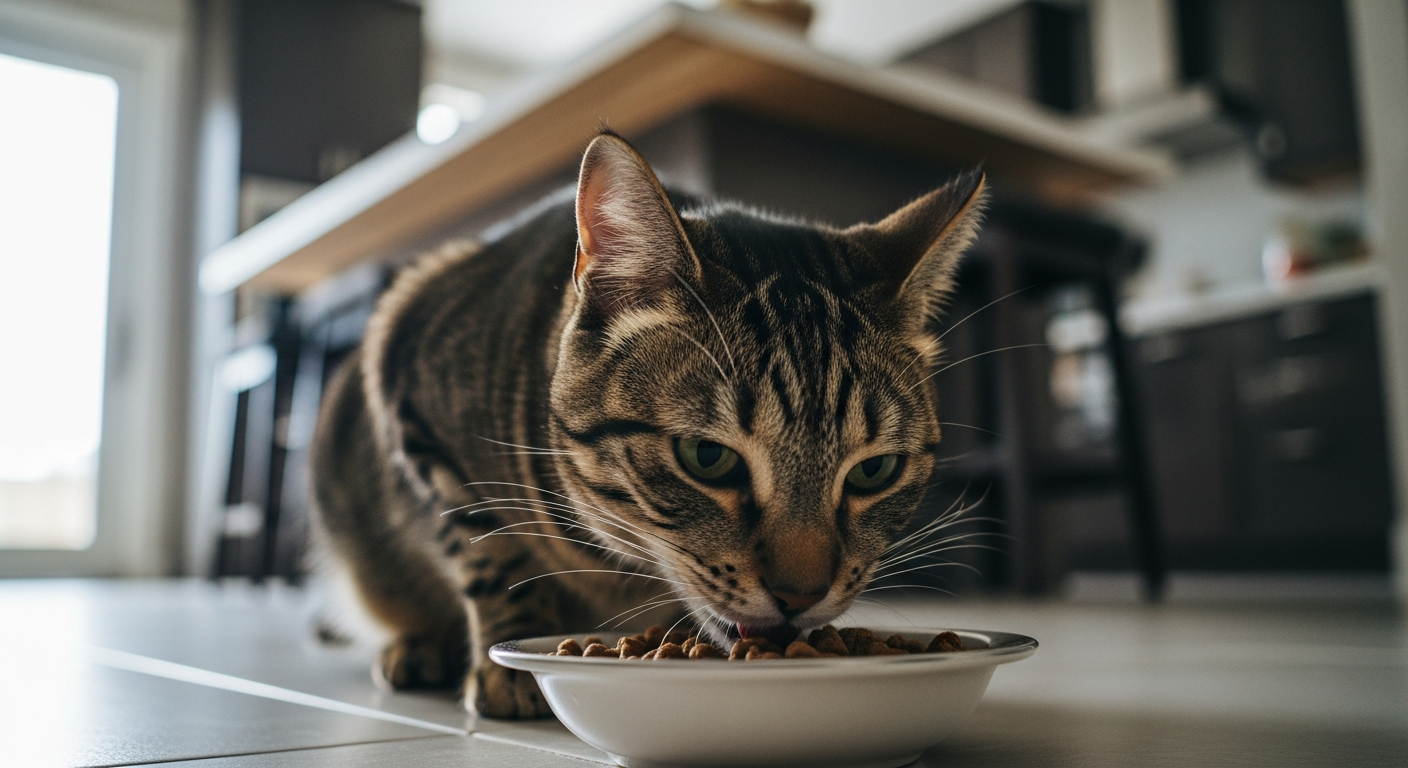

The bond between humans and domestic animals spans centuries, evolving from working relationships to cherished companionship. These animals, ranging from common household pets like dogs and cats to more specialized domestic species, rely on their human caregivers for a structured daily life that supports their physical and mental health. A comprehensive approach to their care involves understanding their natural instincts, providing a stable habitat, and meeting their unique physiological needs.
Understanding Domestic Animal Behavior and Companionship
Domestic animals exhibit a wide range of behaviors influenced by their species, breed, and individual experiences. Observing an animal’s behavior is key to understanding its needs and ensuring its welfare. For instance, dogs thrive on social interaction and routine, often displaying complex social behaviors. Cats, while often perceived as independent, also benefit from consistent companionship and environmental enrichment that caters to their predatory instincts. Providing opportunities for species-appropriate behavior, such as play, exploration, and rest, contributes significantly to their mental well-being and strengthens the human-animal bond.
Essential Nutritional Needs for Domestic Species
Nutrition forms the cornerstone of a domestic animal’s health. Each species has distinct dietary requirements that must be met to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal body condition. For example, a cat’s diet must be rich in animal-based protein and specific amino acids like taurine, which is vital for heart function and vision. Dogs, being omnivores, require a balanced diet of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. The quality and type of food, portion control, and access to fresh water are critical considerations for responsible animal care. Understanding these species-specific nutritional needs helps prevent health issues and supports a long, active life.
Promoting Animal Welfare and Health Through Care
Animal welfare encompasses an animal’s physical and mental state, ensuring they are free from hunger, thirst, discomfort, pain, injury, and disease, and have the freedom to express normal behavior. Regular veterinary care, including vaccinations, parasite control, and routine check-ups, is essential for maintaining health. Beyond medical interventions, daily care involves providing a clean and safe habitat, adequate shelter, and opportunities for exercise tailored to the animal’s species and age. Proactive care helps detect potential health issues early, improving outcomes and ensuring a good quality of life for domestic animals.
The Role of Training and Enrichment in Daily Life
Training and enrichment are vital components of a domestic animal’s daily life, contributing to their overall behavior and health. Training, particularly for species like dogs, establishes clear communication, builds confidence, and ensures safety. Positive reinforcement methods are generally effective, promoting a cooperative relationship. Environmental enrichment involves providing stimulating activities and objects that encourage natural behaviors, such as puzzles for mental engagement or scratching posts for cats. These activities prevent boredom, reduce stress, and can mitigate undesirable behaviors, fostering a more harmonious living environment.
Considering Adoption and Responsible Pet Ownership
Responsible pet ownership begins with the decision to adopt an animal, often from local services or rescue organizations. This process involves a commitment to providing lifelong care, including meeting the animal’s behavioral, nutritional, and health requirements. Understanding the specific needs of different species and breeds before adoption is crucial. For example, some breeds require more exercise, while others need extensive grooming. Responsible ownership also entails understanding the animal’s impact on the local ecosystem and ensuring they are not contributing to wildlife disturbances, particularly in areas near natural habitats. It is a commitment to fostering a positive relationship and ensuring the animal’s welfare throughout its life.
Ensuring the well-being of domestic animals requires a holistic approach that integrates careful daily management, appropriate nutrition, consistent veterinary oversight, and a deep understanding of their unique behavioral needs. By focusing on these key areas, caregivers can provide a nurturing environment that supports both the physical health and emotional welfare of their animal companions, strengthening the mutual benefits of the human-animal relationship.