Holographic Touchscreens: The Future at Your Fingertips
In a world where digital interfaces are ubiquitous, a groundbreaking technology is poised to redefine our interaction with devices. Holographic touchscreens, once confined to the realm of science fiction, are now emerging as a tangible reality. This innovative technology promises to transform how we perceive and interact with digital information, blending the physical and virtual worlds in ways previously unimaginable. As we stand on the cusp of this technological revolution, let's explore the potential of holographic touchscreens and their implications for our digital future.
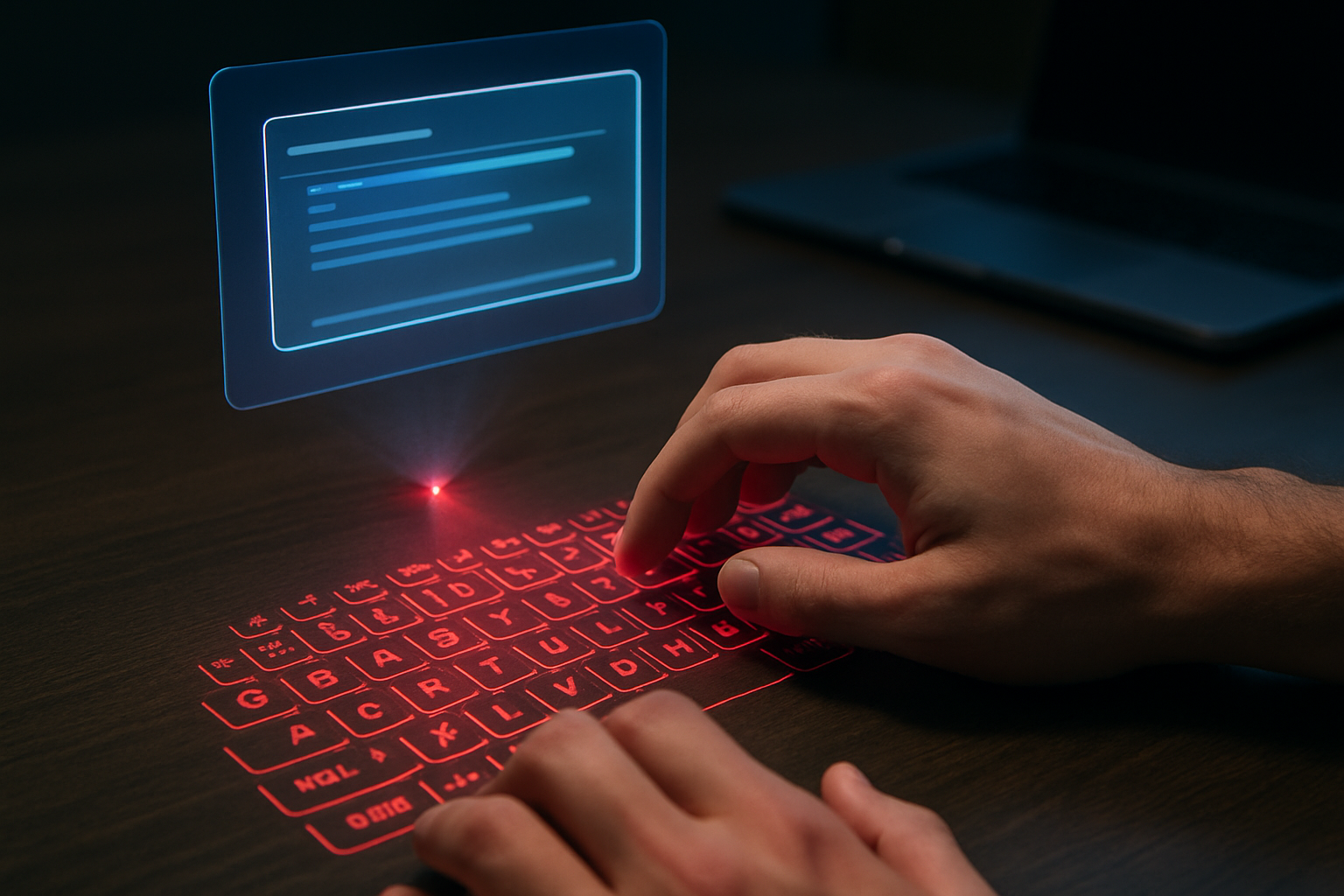

Early prototypes struggled with issues like low resolution, limited viewing angles, and the lack of tactile feedback. However, persistent research and innovation have led to significant improvements in these areas. Today, holographic touchscreens are moving from laboratory experiments to practical applications, with several tech giants and startups racing to bring this technology to market.
How Holographic Touchscreens Work
At the heart of holographic touchscreen technology lies a complex interplay of light manipulation, spatial tracking, and haptic feedback. Unlike traditional displays that project images onto a flat surface, holographic systems create three-dimensional light fields in mid-air. These light fields are generated using a combination of laser projections, micro-mirror arrays, and advanced algorithms that control the interference patterns of light waves.
The ‘touch’ aspect of these screens is achieved through various methods. Some systems use infrared cameras to track hand movements, while others employ ultrasonic waves or air pressure to provide tactile feedback. More advanced prototypes are experimenting with femtosecond lasers to create plasma in the air, which can be felt as a physical sensation when touched.
Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of holographic touchscreens span a wide range of industries. In healthcare, surgeons could manipulate 3D models of organs during pre-operative planning. Architects and engineers could interact with holographic blueprints, making real-time adjustments to their designs. The entertainment industry could create immersive gaming experiences where players physically interact with holographic elements.
Education stands to benefit significantly, with students able to explore complex concepts through interactive 3D models. In retail, customers could virtually try on clothes or visualize furniture in their homes before making a purchase. The technology also holds promise for enhancing remote collaboration, allowing team members in different locations to interact with the same holographic objects as if they were in the same room.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the exciting potential, holographic touchscreens face several challenges before widespread adoption becomes feasible. One of the primary hurdles is power consumption. Creating and maintaining holographic images requires significant energy, which can be a limiting factor for mobile devices. Additionally, the need for specialized hardware and environments to generate stable holograms currently restricts the technology’s portability.
Another challenge lies in developing intuitive user interfaces for 3D interactions. While we’re accustomed to tapping and swiping on 2D screens, manipulating objects in 3D space requires new interaction paradigms and user training. There’s also the question of eye strain and potential long-term effects of prolonged exposure to holographic displays, which necessitates further research and safety standards.
The Road Ahead
As research progresses, we can expect to see holographic touchscreens become more refined and accessible. Current estimates suggest that consumer-grade holographic devices could hit the market within the next 5-10 years, with prices initially ranging from $1,000 to $5,000 for personal devices. However, as with most emerging technologies, costs are likely to decrease as production scales up and the technology matures.
The impact on the global display market could be significant, with analysts predicting that holographic technologies could capture a substantial portion of the $150 billion display industry by 2030. This shift would not only disrupt existing markets but also create new opportunities for software developers, content creators, and hardware manufacturers specializing in holographic interfaces.
Ethical and Social Implications
As we embrace this new form of digital interaction, it’s crucial to consider the ethical and social implications. Holographic touchscreens have the potential to blur the lines between physical and digital realities even further, raising questions about privacy, digital addiction, and the nature of human interaction in an increasingly virtual world.
There’s also the issue of accessibility and the potential for creating new digital divides. As holographic interfaces become more prevalent in professional and educational settings, ensuring equal access to this technology will be vital to prevent exacerbating existing inequalities.
In conclusion, holographic touchscreens represent a leap forward in human-computer interaction, offering a more intuitive and immersive way to engage with digital content. While challenges remain, the potential benefits across various sectors are immense. As this technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly reshape our digital landscape, opening up new possibilities for innovation and creativity in the years to come.