Implementing Circular Economy Models in Production
The traditional linear economic model, often characterized by a 'take-make-dispose' approach, is increasingly being challenged by resource scarcity, environmental concerns, and evolving consumer expectations. In response, businesses worldwide are exploring and adopting circular economy models, which aim to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extract the maximum value from them while in use, then recover and regenerate products and materials at the end of each service life. This paradigm shift requires a fundamental rethinking of production processes, supply chains, and overall business strategy, moving towards a more sustainable and resilient industrial future.
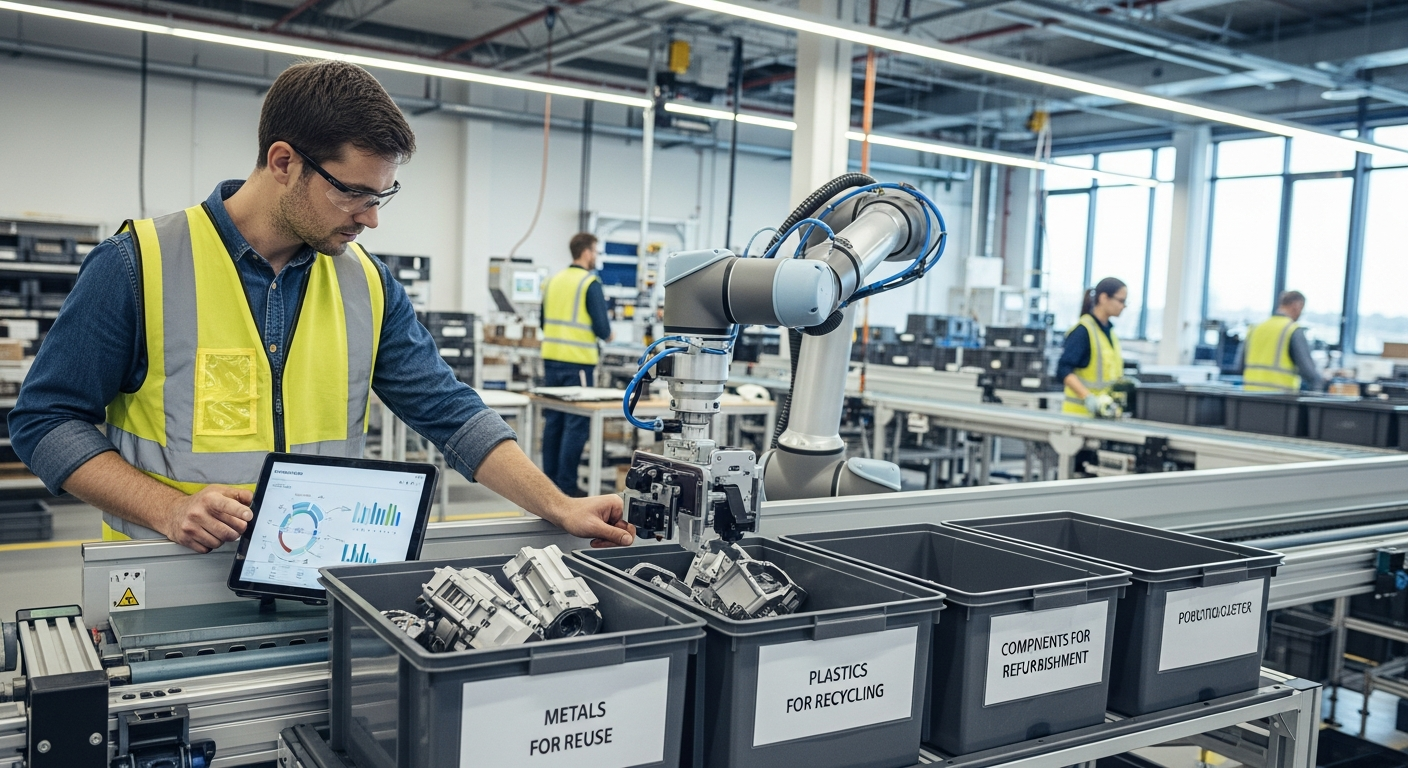

Understanding Circular Economy in Production Operations
Implementing circular economy principles within production operations involves a holistic approach that redefines how goods are designed, manufactured, and utilized. At its core, it focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency throughout the entire product lifecycle. This includes designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, as well as integrating closed-loop systems for materials. Businesses are increasingly recognizing that embedding sustainability into their core operations is not just an environmental imperative but also a driver for innovation and competitive advantage, influencing everything from material sourcing to end-of-life management.
Key Strategies for Sustainable Manufacturing and Supply
Achieving sustainable manufacturing and supply requires deliberate strategic development. Companies are exploring various approaches, such as industrial symbiosis, where waste from one process becomes a raw material for another. Product-as-a-service models are also gaining traction, shifting ownership from consumer to producer, thereby incentivizing manufacturers to design for longevity and easy maintenance. Furthermore, optimizing production efficiency through lean manufacturing principles helps reduce material consumption and energy use, contributing significantly to circular goals. The emphasis is on creating value through resource preservation and regeneration, fostering long-term growth and market resilience.
Leveraging Technology and Automation for Circularity
Technology and automation play a pivotal role in enabling circular economy models. Advanced digital tools, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) for tracking materials and products, artificial intelligence (AI) for optimizing processes, and blockchain for supply chain transparency, provide crucial insights. Robotics can facilitate disassembly, sorting, and recycling processes with greater precision and efficiency. These innovations support better resource management, from predictive maintenance that extends equipment life to smart recycling systems that maximize material recovery. Embracing these technological advancements is essential for enterprises looking to scale their circular initiatives.
Reimagining Logistics and Supply Chain Processes
Effective logistics and reimagined supply chain processes are fundamental to a functioning circular economy. This involves developing robust reverse logistics networks capable of collecting used products and materials for refurbishment, remanufacturing, or recycling. Designing supply chains that can handle both forward and backward flows efficiently is complex but vital. Companies must collaborate with suppliers, customers, and third-party logistics providers to establish seamless material loops. This focus on optimizing the flow of resources, rather than just products, helps reduce waste and ensures that valuable materials remain within the economic system.
Market Growth and Enterprise Strategy for Circular Models
The shift towards circular economy models presents significant opportunities for market growth and requires a clear enterprise strategy. Businesses that successfully adopt circular practices can unlock new revenue streams through remanufactured products, repair services, or material recovery. Beyond direct financial benefits, a strong commitment to sustainability can enhance brand reputation, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and improve stakeholder relations. Furthermore, proactive engagement with circular principles can help companies navigate evolving regulatory landscapes and position themselves as leaders in a future-oriented trade environment, fostering long-term development.
Building a Culture of Innovation and Efficiency
To fully embed circular economy principles, organizations must cultivate a culture of continuous innovation and efficiency. This means encouraging employees to identify opportunities for resource optimization, waste reduction, and material reuse across all departments. Investing in training and development programs can equip teams with the skills needed to design circular products, manage complex supply chains, and implement advanced digital analytics tools. By fostering an environment where new ideas are welcomed and tested, businesses can drive ongoing improvements in their production processes, leading to greater sustainability and operational resilience.
Implementing circular economy models in production represents a transformative journey for businesses globally. It demands a strategic re-evaluation of current practices, a willingness to adopt new technologies, and a commitment to collaborative innovation across the value chain. By focusing on resource efficiency, waste reduction, and material regeneration, companies can not only mitigate environmental impact but also unlock new avenues for economic growth and long-term sustainability.